

Let's say I already had some dummy text in my text.txt file when I first created it: write() method and run your code, any text you previously had will be overwritten. It's important to note that each time you use the.
#PYTHON WRITE TO FILE CODE#
Open the built-in terminal in Visual Studio Code ( Control ~) and run the code by typing: python3 scripts.py.Ĭheck out text.txt and it should have the following added to it: Write to an Existing File in Python If the file you want to write to exists already, and you want to add additional lines to it, you'll need to open it using the a parameter for 'append.' with open( 'testfile. To add the text on different lines, like I have done in the example above, you have to explicitly add in the newline character, \, yourself.

So, to add some text to the text file, in scripts.py add: with open("text.txt","w") as file:įile.write("And I want to add more lines to say how much I like it") write() method is used for writing in the text file and adding in the string contents you want.
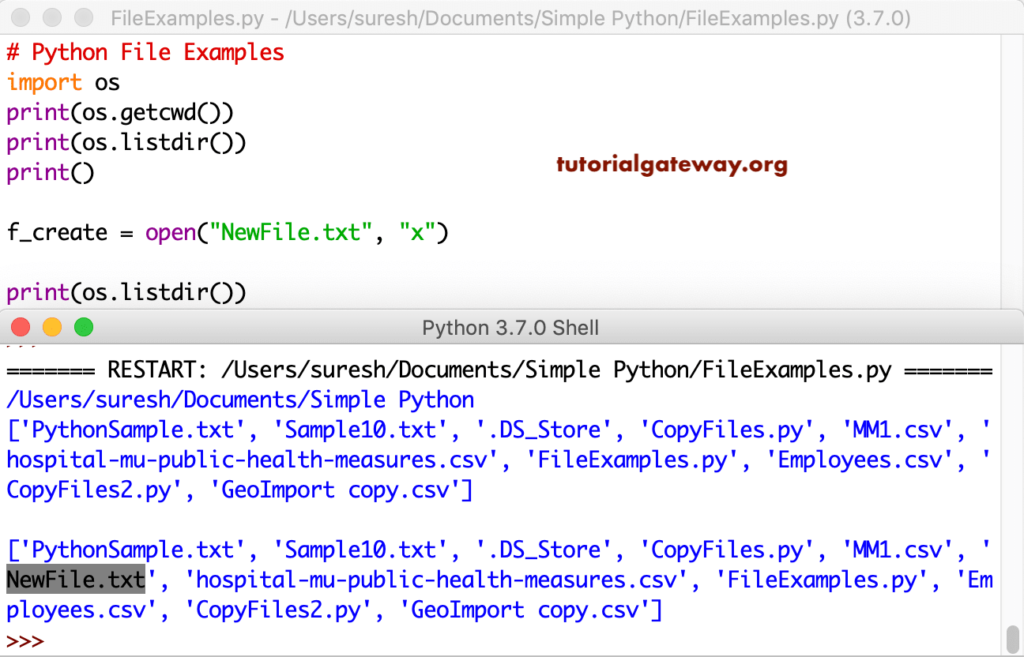
To write to files, the mode is w for write. The second parameter is the mode in which the file will be opened. Second, write to the text file using the write() or writelines() method. The file in this example is in the same directory as the Python script, so the path is simple. First, open the text file for writing (or append) using the open() function. The open() function returns a file object and takes in two parameters: The path to the file and the name of the file itself that you want to open.
#PYTHON WRITE TO FILE HOW TO#
#create two empty files in the same directory: one text file and one to hold your Python scriptsĪDVERTISEMENT How to write to text files in Python #move into the directory you just created
#create a new directory and give it a name #this command moves you into your home directory if you're not there already I am creating the project in my home directory. The first step is to set up the project's directory structure.Ĭhoose a place where you want to create a new directory and follow the steps below. Let's get started! How to set up the project's structure You can follow along with me and go through the same steps I do. In this article, I'll create a simple project where I'll write to, append to, and then finally at the end read from a text file in Python to show you how it's done. The handle is positioned at the end of the file. The file is created if it does not exist. The definition of these access modes is as follows: Append Only (‘a’): Open the file for writing. Reading, writing, and editing files in Python is a common task, since the language provides us with built-in functions that allow us to do so. In order to append a new line to the existing file, open the file in append mode, by using either ‘a’ or ‘a+’ as the access mode. Then you can easily access that data at any point.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
